Evaluate the probability mass function of a hurdle Poisson distribution
Source:R/HurdlePoisson.R
pdf.HurdlePoisson.RdEvaluate the probability mass function of a hurdle Poisson distribution
Arguments
- d
A
HurdlePoissonobject created by a call toHurdlePoisson().- x
A vector of elements whose probabilities you would like to determine given the distribution
d.- drop
logical. Should the result be simplified to a vector if possible?
- elementwise
logical. Should each distribution in
dbe evaluated at all elements ofx(elementwise = FALSE, yielding a matrix)? Or, ifdandxhave the same length, should the evaluation be done element by element (elementwise = TRUE, yielding a vector)? The default ofNULLmeans thatelementwise = TRUEis used if the lengths match and otherwiseelementwise = FALSEis used.- ...
Arguments to be passed to
dhpois. Unevaluated arguments will generate a warning to catch mispellings or other possible errors.
Value
In case of a single distribution object, either a numeric
vector of length probs (if drop = TRUE, default) or a matrix with
length(x) columns (if drop = FALSE). In case of a vectorized distribution
object, a matrix with length(x) columns containing all possible combinations.
Examples
## set up a hurdle Poisson distribution
X <- HurdlePoisson(lambda = 2.5, pi = 0.75)
X
#> [1] "HurdlePoisson(lambda = 2.5, pi = 0.75)"
## standard functions
pdf(X, 0:8)
#> [1] 0.250000000 0.167672793 0.209590992 0.174659160 0.109161975 0.054580987
#> [7] 0.022742078 0.008122171 0.002538178
cdf(X, 0:8)
#> [1] 0.2500000 0.4176728 0.6272638 0.8019229 0.9110849 0.9656659 0.9884080
#> [8] 0.9965302 0.9990683
quantile(X, seq(0, 1, by = 0.25))
#> [1] 0 0 2 3 Inf
## cdf() and quantile() are inverses for each other
quantile(X, cdf(X, 3))
#> [1] 3
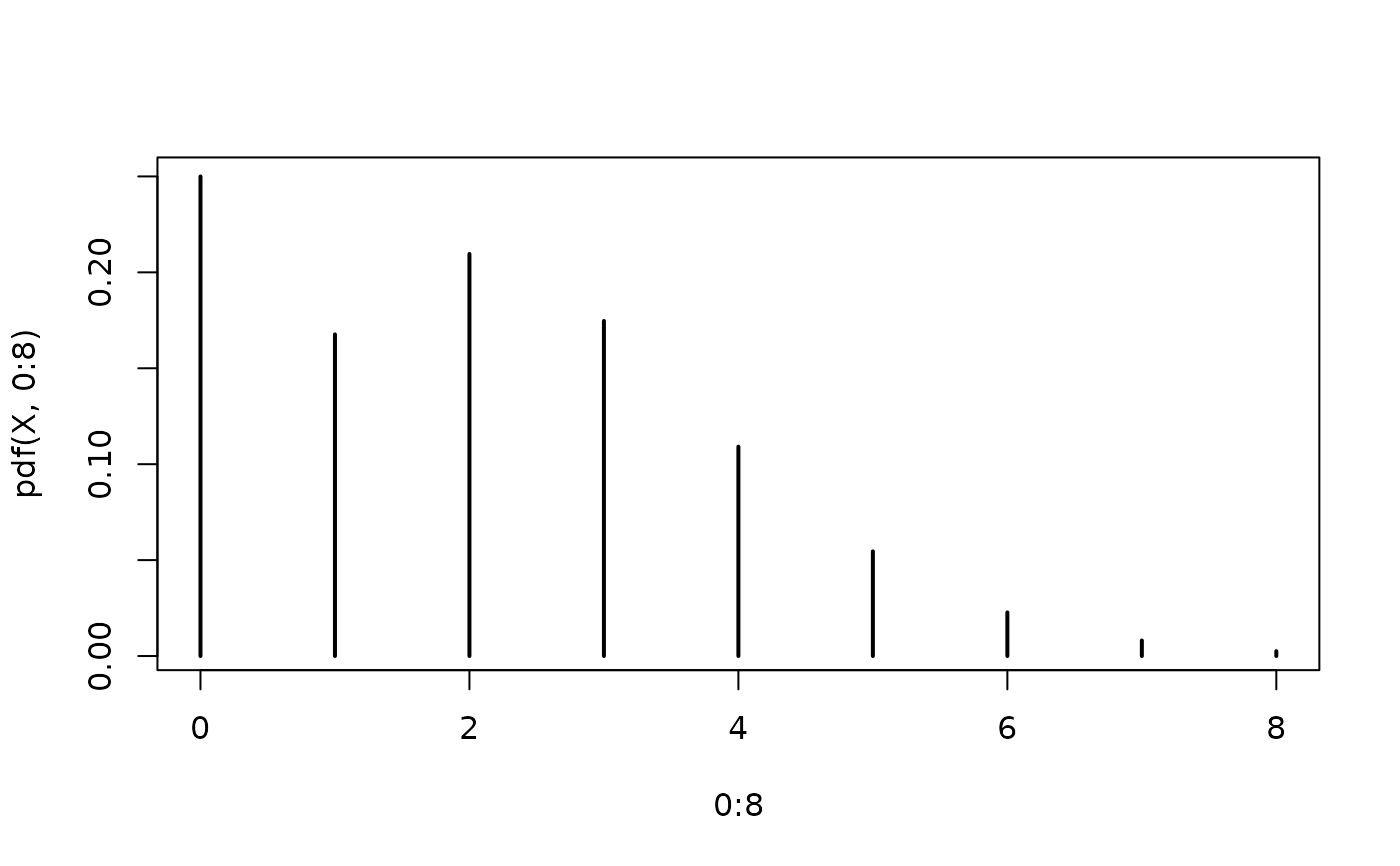
## density visualization
plot(0:8, pdf(X, 0:8), type = "h", lwd = 2)
 ## corresponding sample with histogram of empirical frequencies
set.seed(0)
x <- random(X, 500)
hist(x, breaks = -1:max(x) + 0.5)
## corresponding sample with histogram of empirical frequencies
set.seed(0)
x <- random(X, 500)
hist(x, breaks = -1:max(x) + 0.5)